As of June 30, 2024, the National Health Commission (NHC) issued A nnouncement No. 2 of 202 4, approving a total of 23 products, including new food raw materials (novel food), new food additives, and new food-related products (new food contact substances).
Notably, six new food raw materials were approved: Dendrobium protocorm, Meso-zeaxanthin, Pichia kluyveri, Bacillus subtilis DE111, L-alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine, and Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides.
In addition, according to information released by the NHC and the China National Center for Food Safety Risk Assessment (CFSA), in the first half of 2024, applications for 16 new food raw materials were accepted, seven draft announcements were issued for public comment, and one substance was added to the list for termination of review.
In this article, the food team at CIRS Group provides an overview of the acceptance and approval status of new food raw materials in China for the first half of 2024.
List of new food raw materials accepted in the first half of 2024 (16 types)
In the first half of 2024, China’s NHC accepted the applications for 16 new food raw materials. Among these, only four were imported, with the majority being domestically produced. The technical review status of each product is as follows:
|
S.N. |
Date of acceptance |
Acceptance No. |
Name |
Review status |
|
1 |
January 2, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0001 |
Acer truncatum |
Delivered an extension notice on February 6, 2024 |
|
2 |
January 2, 2024 |
衛食新進申字(2024) No. 0001 |
Comb extract |
Delivered an extension notice on February 6, 2024 |
|
3 |
January 2, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0002 |
Gardenia oil |
Delivered an extension notice on February 6, 2024 |
|
4 |
March 13, 2024 |
衛食新進申字(2024) No. 0002 |
Brewer’s yeast CNCM I-3799 |
Delivered an extension notice on April 2, 2024 |
|
5 |
January 5, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0003 |
Camellia chrysantha cell culture |
Delivered an extension notice on February 6, 2024 |
|
6 |
March 18, 2024 |
衛食新進申字(2024) No. 0003 |
Lutein easter |
Delivered an extension notice on April 2, 2024 |
|
7 |
March 14, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0004 |
Luohanshen |
Delivered an extension notice on April 2, 2024 |
|
8 |
April 29, 2024 |
衛食新進申字(2024) No. 0004 |
Lemon Myrtle |
Delivered an extension notice on May 30, 2024 |
|
9 |
March 21, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0005 |
Tender leaf seedlings of CARTHAMI FLOS |
Delivered an extension notice on April 2, 2024 |
|
10 |
May 10, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0006 |
Pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium salt |
Delivered an extension notice on May 30, 2024 |
|
11 |
May 15, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0007 |
Camelina sativa seed oil |
Delivered an extension notice on May 30, 2024 |
|
12 |
May 17, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0008 |
Cis-15-Tetracosenoic Acid |
Delivered an extension notice on June 4, 2024 |
|
13 |
May 17, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0009 |
L-Ergothioneine |
Delivered an extension notice on May 30, 2024 |
|
14 |
May 20, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0010 |
Bacillus subtilis QK02 |
Delivered an extension notice on June 4, 2024 |
|
15 |
June 13, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0011 |
Luohanshen |
Under review |
|
16 |
June 20, 2024 |
衛食新申字(2024) No. 0012 |
Xiangyu peony |
Under review |
List of new food raw materials issued for public comment in the first half of 2024 (seven types)
In the first half of 2024, seven new food raw materials passed the technical review of CFSA and were issued for public comment. This includes a revision of the announcement regarding the approved new food raw material, rye pollen (No. 3 of 2023). Details are as follows:
Maritime pine bark extract (draft announcement)
|
Name |
Maritime pine bark extract |
|
Basic information |
Source: Pinus pinaster Aiton |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Prepared through grinding, extraction, filtration, concentration, drying, and other processes using maritime pine bark extract as the raw material. |
|
Recommended intake |
≤ 150 mg/day |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on December 23, 2021. Acceptance No.: 衛食新進申字(2021) No. 0012. Acceptance name: Maritime pine bark extract (Product name: Bi Rong Jian®) |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on March 1, 2024. |
Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis M-63 (draft announcement)
|
Name |
Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis M-63 |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on November 6, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新進申字 (2023) No. 0004. Acceptance name: Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis M-63 |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on March 1, 2024. |
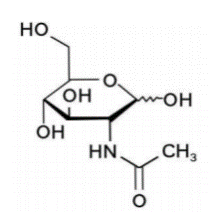
N-acetylglucosamine (draft announcement)
|
Name |
N-acetylglucosamine |
|
Basic information |
Structure:
CAS number: 7512-17-6 Molecular formula: C8H15NO6 Molecular weight: 221.21 |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Prepared through the fermentation of Corynebacterium glutamicum RDG-2110, followed by filtration, concentration, crystallization, centrifugation, alcohol washing, drying, and other processes using glucose, corn syrup powder, ammonium sulfate, potassium phosphate monobasic, and magnesium sulfate as raw materials. |
|
Recommended intake |
≤500 mg/day |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on April 6, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2023) No. 0005. Acceptance name: N-acetylglucosamine |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on March 1, 2024. |
Nannochloropsis oil (draft announcement)
|
Name |
Nannochloropsis oil |
|
Basic information |
Source: Nannochloropsis gaditana |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Prepared through ethanol extraction, filtration, purification, concentration, and other processes using Nannochloropsis gaditana as the raw material. |
|
Recommended intake |
≤ 2 g/day |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on September 4, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2023) No. 0013. Acceptance name: Nannochloropsis oil |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on April 28, 2024. |
Rye pollen (draft announcement)
|
Name |
Rye pollen |
|
Other information |
Rye pollen was approved as a new food raw material in Announcement No. 3 of 2023 by the NHC. Based on industry data and reviewed by the Expert Review Committee, it is now proposed to revise the dietary fiber content requirement in the announcement to be ≥30%. |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on April 28, 2024. |
Egg yolk phospholipid and protein (draft announcement)
|
Name |
Egg yolk phospholipid and protein |
|
Basic information |
Source: Egg yolk powder |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Prepared through granulation, supercritical CO2 extraction, separation, and other processes using egg yolk powder as the raw material. |
|
Recommended intake |
≤ 5 g/day |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on August 28, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2023) No. 0011. Acceptance name: Egg yolk phospholipid |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on April 28, 2024. |
Stevia leaf polyphenols (draft announcement)
|
Name |
Stevia leaf polyphenols |
|
Basic information |
Source: Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Prepared through ethanol extraction, filtration, concentration, drying, and other processes by using stevia leaves as the raw material. |
|
Recommended intake |
≤500 mg/day (expressed as total polyphenols) |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on September 7, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2023) No. 0015. Acceptance name: Stevia extract |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on June 14, 2024. |
List of approved new food raw materials in the first half of 2024 (six types)
Among the six new food raw materials approved in the first half of 2024 are three strains that can be used in food: Pichia kluyveri, Bacillus subtilis DE111, and Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroide. Notably, in terms of safety considerations, Bacillus subtilis DE111 is the first strain to be included in the List of Strains that Can Be Used in Food under its strain number. Detailed approval information for each product is as follows:
Dendrobium protocorm
|
Name |
Dendrobium protocorm |
|
Basic information |
Source: Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo or Dendrobium huoshanense C. Z. Tang et S. J. Cheng |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Protocorms are obtained through tissue culture using the seeds or stem of Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo or Dendrobium huoshanense C. Z. Tang et S. J. Cheng as raw materials, followed by collection, drying, and other processes. |
|
Recommended intake |
Dehydrated products ≤ 3.5g/day |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
(1) Date of acceptance: unknown. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2010) No. 0027. Acceptance name: Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo germ culture (2) Date of acceptance: unknown. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2012) No. 0009. Acceptance name: Dendrobium huoshanense C. Z. Tang et S. J. Cheng protocorm (3) Accepted on October 10, 2019. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2019) No. 0002. Acceptance name: Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo protocorm |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on December 25, 2019. |
|
Date of official approval |
Officially approved on March 13, 2024, according to Announcement No. 2 of 2024. |
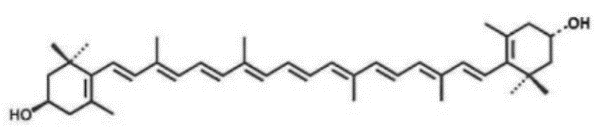
Meso-zeaxanthin
|
Name |
Meso-zeaxanthin |
|
Basic information |
Source: Tagetes erecta L. Structure:
CAS number: 31272-50-1 Molecular formula: C40H56O2 Molecular weight: 568.88 |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Prepared through dehydration, grinding, extraction, isomerization, purification, and other processes using flowers of Tagetes erecta L. as the raw material. |
|
Recommended intake |
≤ 8 mg/day (expressed as Meso-zeaxanthin) |
|
Other information |
1) The applicable scope of use does not include food for infants and young children. 2) The detection method for n-Hexane residue must follow the provisions of GB 24405. 3) Food safety indicators must comply with the requirements specified in the official announcement. |
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on March 17, 2022. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2022) No. 0002. Acceptance name: Meso-zeaxanthin |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on August 28, 2023. |
|
Date of official approval |
Officially approved on March 13, 2024, according to Announcement No. 2 of 2024. |
Pichia kluyveri
|
Name |
Pichia kluyveri |
|
Other information |
1) Being included in the List of Strains that Can Be Used in Food and approved for the use in fermentation processing of fermented wine, fruit and vegetable juices, and tea drinks (excluding food for infants and young children). The labels and instructions must bear a statement of the scope of use. 2) Food safety indicators must comply with the requirements specified in GB 31639-2023 National Food Safety Standard - Strain Preparation for Food Processing. |
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on December 5, 2022. Acceptance No.: 衛食新進申字(2022) No. 0006. Acceptance name: Pichia kluyveri |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on August 28, 2023. |
|
Date of official approval |
Officially approved on March 13, 2024, according to Announcement No. 2 of 2024. |
Bacillus subtilis DE111
|
Name |
Bacillus subtilis DE111 |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on March 9, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2023) No. 0003. Acceptance name: Bacillus subtilis |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on August 28, 2023. |
|
Date of official approval |
Officially approved on March 13, 2024, according to Announcement No. 2 of 2024. |
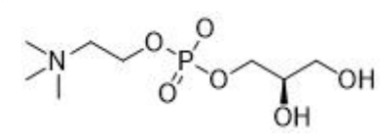
L-alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine
|
Name |
L-alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine |
|
Basic information |
Structure:
CAS number: 28319-77-9 Molecular formula: C8H20NO6P Molecular weight: 257.22 |
|
Brief introduction of the production process |
Prepared through condensation and esterification reactions, followed by decolorization, impurity removal, concentration, refinement, drying, and other processes using polyphosphoric acid, choline chloride, R-3-Chloro-1,2-propanediol, sodium hydroxide and water as raw materials. |
|
Recommended intake |
≤600 mg/day (on dry mass) |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on September 6, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2023) No. 0014. Acceptance name: L-alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on December 22, 2023. |
|
Date of official approval |
Officially approved on March 13, 2024, according to Announcement No. 2 of 2024. |
Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides
|
Name |
Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides |
|
Other information |
|
|
Date of acceptance |
Accepted on September 11, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新進申字 (2023) No. 0002. Acceptance name: Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides |
|
Date of public consultation |
Passed the technical review and issued for public comment on December 22, 2023. |
|
Date of official approval |
Officially approved on March 13, 2024, according to Announcement No. 2 of 2024. |
Food raw materials included in the list for termination of review in the first half of 2024 (one type)
In the first half of 2024, one food raw material, L-Theanine, was included in the termination of review list. The list now includes 74 products.
L-Theanine
|
Name |
L-Theanine |
|
Review opinion |
Theanine was approved as a new food raw material in Announcement No. 15 of 2014 by the former National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC). This product is substantially equivalent to the approved L-Theanine, suggesting termination of review. Food safety indicators should comply with HNC Announcement No. 4 of 2023, with solvent residue divinylbenzene ≤ 50 μg/kg. |
|
Acceptance date and number |
Accepted on September 4, 2023. Acceptance No.: 衛食新申字(2023) No. 0012. Acceptance name: L-Theanine |
Conclusion
Compared to the same period in 2023, the number of applications accepted in the first half of this year has seen a significant increase (16), nearly matching the total accepted for the entire year of 2023 (22). Furthermore, it can be seen from the application process of the six raw materials that the overall review time is decreasing, with two products having application cycles of approximately six months each. CIRS Group advises that enterprises intending to apply should focus on material preparation, which not only shortens the review cycle but also helps enterprises save time and costs.
For updates on the acceptance, public consultation, and approval announcements regarding new food raw materials, you can use “ChinaFoodDB”, the comprehensive digital intelligent query platform for food raw materials and additives developed by CIRS. Click here to use it for free!
If you need any assistance or have any questions, please get in touch with us via service@jianzaoshiwang.cn.
(Note: There may be omissions and inaccuracies in the data. The data in this article is for reference only, please refer to the official information released by government departments. CIRS Group welcomes any corrections.)